Join us on a captivating journey through the fascinating world of animal cells with our comprehensive guide, “Tour of an Animal Cell Structures and Functions BioFlix Tutorial.” This tutorial will unravel the intricate inner workings of these fundamental units of life, providing an immersive experience that illuminates their remarkable complexity.
Delve into the depths of animal cell structures, exploring their diverse functions and intricate relationships. Discover the secrets of the cell membrane, the nucleus, mitochondria, and a myriad of other organelles, each playing a vital role in maintaining cellular harmony.
Introduction to Animal Cell Structures and Functions
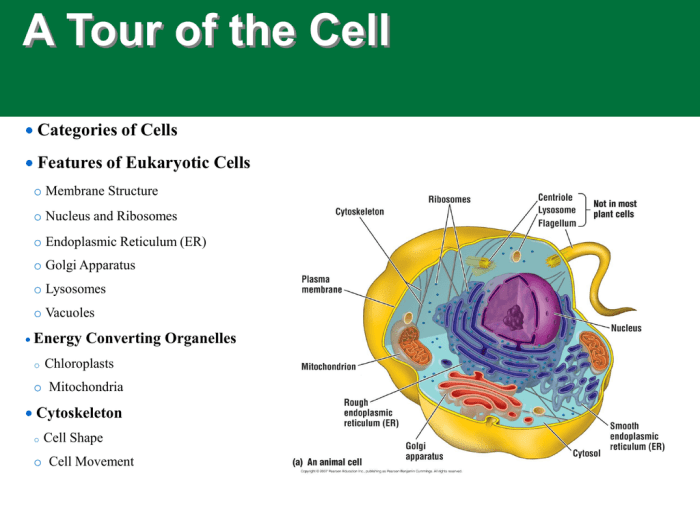
Animal cells are the fundamental building blocks of all animals. They are responsible for carrying out the essential functions of life, such as metabolism, growth, reproduction, and communication. Understanding the structures and functions of animal cells is crucial for comprehending the biology of animals and the principles of life itself.
Tour of Animal Cell Structures
Animal cells are complex structures composed of various organelles, each with a specific function. Here is a comprehensive table outlining the key structures of an animal cell:
| Structure | Function | Location | Image/Diagram |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cell Membrane | Controls the movement of substances into and out of the cell | Surrounds the cell | [Diagram sel dengan membran sel berlabel] |
| Cytoplasm | Contains the organelles and other cellular components | Between the cell membrane and nucleus | [Diagram sel dengan sitoplasma berlabel] |
| Nucleus | Contains the cell’s genetic material (DNA) | In the center of the cell | [Diagram sel dengan nukleus berlabel] |
| Nucleolus | Site of ribosome production | Inside the nucleus | [Diagram sel dengan nukleolus berlabel] |
| Ribosomes | Site of protein synthesis | Attached to the endoplasmic reticulum or free in the cytoplasm | [Diagram sel dengan ribosom berlabel] |
| Endoplasmic Reticulum | Folds and transports proteins | Network of membranes throughout the cytoplasm | [Diagram sel dengan retikulum endoplasma berlabel] |
| Golgi Apparatus | Modifies and packages proteins | Stack of flattened sacs | [Diagram sel dengan aparatus Golgi berlabel] |
| Lysosomes | Breaks down waste products | Small sacs filled with digestive enzymes | [Diagram sel dengan lisosom berlabel] |
| Vacuoles | Stores materials for the cell | Membrane-bound sacs | [Diagram sel dengan vakuola berlabel] |
| Mitochondria | Produces energy for the cell | Rod-shaped organelles | [Diagram sel dengan mitokondria berlabel] |
| Chloroplasts (if applicable) | Site of photosynthesis (in plant cells) | Green organelles | [Diagram sel dengan kloroplas berlabel] |
Interdependence of Cell Structures: Tour Of An Animal Cell Structures And Functions Bioflix Tutorial
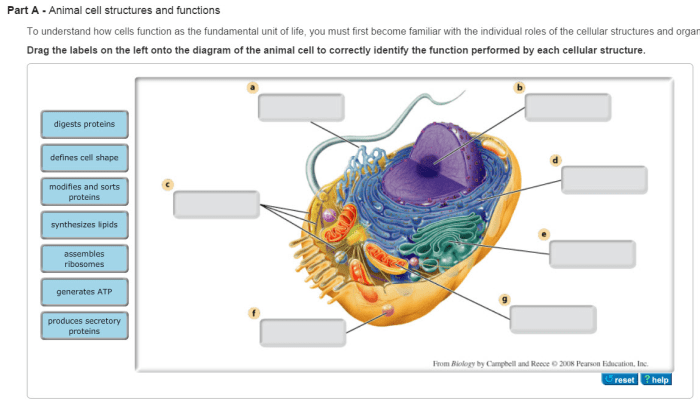
The structures of an animal cell are highly interdependent and work together to maintain cell homeostasis. Each organelle has a specific function, and disruptions in one structure can affect the functioning of others. For example, damage to the cell membrane can impair the movement of nutrients and waste products, which can lead to cell death.
Animal Cell Functions
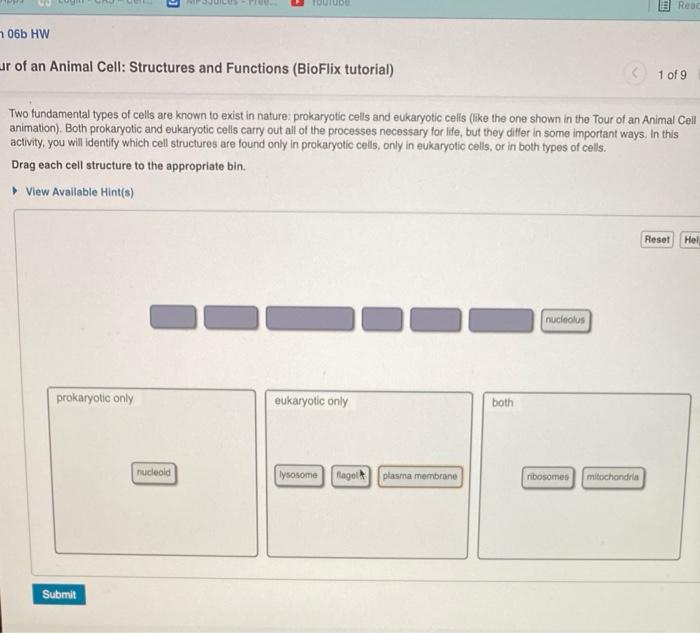
Animal cells perform a wide range of functions essential for life. These functions include:
- Metabolism: Breaking down nutrients to release energy
- Growth and reproduction: Creating new cells for growth and repair
- Communication: Sending and receiving signals to coordinate activities
- Movement: Using energy to move or transport substances
Comparing Animal and Plant Cells
| Structure/Function | Animal Cell | Plant Cell |
|---|---|---|
| Cell Wall | Absent | Present |
| Chloroplasts | Absent | Present |
| Vacuoles | Small and numerous | Large and central |
| Centrosomes | Present | Absent |
| Reproduction | Mitosis and meiosis | Mitosis only |
Applications of Cell Biology
Cell biology has a wide range of applications in various fields, including:
- Medicine: Developing treatments for diseases by understanding cell processes
- Biotechnology: Engineering cells for industrial purposes
- Environmental science: Studying the impact of pollutants on cells
FAQ Compilation
What are the key characteristics of animal cells?
Animal cells are eukaryotic cells, meaning they possess a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. They lack a cell wall and chloroplasts, distinguishing them from plant cells.
How do cell structures contribute to cell homeostasis?
Cell structures work in concert to maintain a stable internal environment within the cell. They regulate the movement of nutrients and waste products, facilitate chemical reactions, and ensure the proper functioning of cellular processes.
What are some examples of how disruptions in cell structures can lead to cell dysfunction?
Disruptions in cell structures can lead to a cascade of events that impair cellular function. For instance, damage to the cell membrane can disrupt the cell’s ability to regulate the passage of substances, leading to cell death.