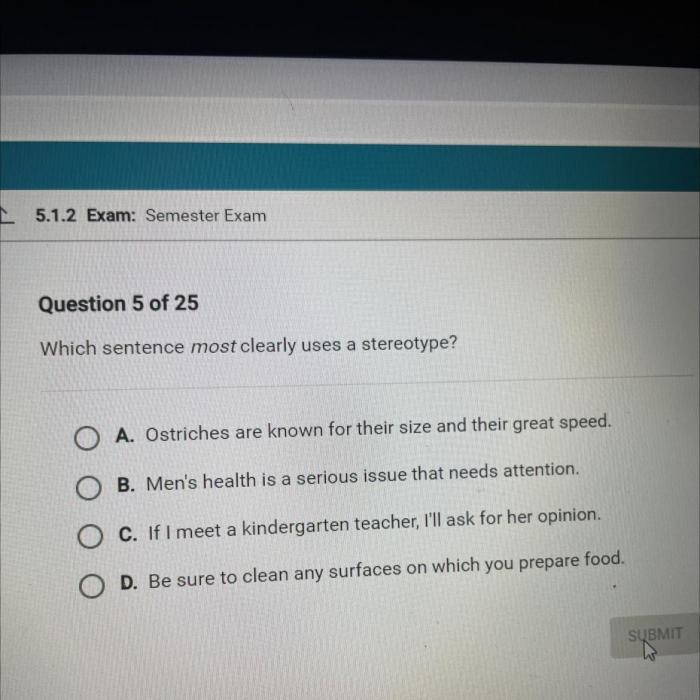
Which statement is most clearly objective? This question lies at the heart of our understanding of language and its ability to convey information without bias or subjectivity. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of objective language, exploring its defining characteristics, contrasting it with subjective statements, and providing practical criteria for evaluating the objectivity of statements.
By the end of this journey, you will be equipped with the knowledge and skills to navigate the complexities of language and identify objective statements with confidence.
Objectivity in language is a fundamental principle that ensures clarity, accuracy, and precision in communication. It involves the use of language that is free from personal opinions, emotions, or biases. Objective statements are based on facts, evidence, and verifiable information, allowing readers to form their own interpretations without being influenced by the author’s perspective.
Objectivity in Language

Objectivity in language refers to the use of language that is unbiased, factual, and free from personal opinions or emotions. It aims to convey information in a clear and neutral manner, without influencing the reader’s perspective.
Objective language is characterized by the following features:
- Accuracy: It presents facts and information that are true and verifiable.
- Neutrality: It avoids expressing opinions or biases, and presents both sides of an argument fairly.
- Specificity: It uses precise and specific language, avoiding generalizations or vague statements.
- Clarity: It is written in a clear and concise manner, avoiding jargon or technical terms that may be unfamiliar to the reader.
Examples of objective statements include:
- “The Earth’s average temperature has increased by 1 degree Celsius in the last century.”
- “The population of the United States is estimated to be 332 million.”
- “The chemical formula for water is H2O.”
Subjectivity vs. Objectivity, Which statement is most clearly objective
Subjectivity in language refers to the use of language that expresses personal opinions, emotions, or biases. It is often influenced by the writer’s perspective, beliefs, and experiences.
Subjective statements are typically characterized by:
- Opinionated: They express the writer’s personal views or beliefs.
- Emotional: They convey feelings or emotions, rather than facts.
- Biased: They present a one-sided perspective, often omitting or downplaying opposing views.
- Vague: They use general or ambiguous language, leaving room for interpretation.
Examples of subjective statements include:
- “I believe that climate change is the most pressing issue facing our planet today.”
- “The new movie was absolutely terrible.”
- “I think that all politicians are corrupt.”
Bias plays a significant role in subjective statements. Bias refers to the tendency to favor one perspective over others, often based on personal beliefs, experiences, or group affiliations. Bias can lead to distorted or inaccurate information being presented as objective.
Identifying Objective Statements
To identify objective statements, it is important to consider the following key features:
- Factual: The statement is based on verifiable facts and evidence.
- Neutral: The statement does not express any opinions or biases.
- Specific: The statement uses precise and specific language, avoiding generalizations.
- Clear: The statement is written in a clear and concise manner, avoiding jargon or technical terms.
A structured approach to analyzing the objectivity of statements involves:
- Examining the source of the statement: Is it a reputable and unbiased source?
- Considering the context: What is the purpose of the statement? Is it intended to inform or persuade?
- Evaluating the language: Is the statement factual, neutral, specific, and clear?
- Looking for evidence: Is the statement supported by verifiable facts or evidence?
Applications of Objectivity
Objectivity in language is crucial in various contexts, including:
- Scientific research: Objective language is essential for reporting scientific findings accurately and without bias.
- Journalism: Objective reporting is vital for providing accurate and unbiased information to the public.
- Decision-making: Objective analysis of information is necessary for making informed and rational decisions.
Relying on subjective statements can have negative consequences, such as:
- Misinformation: Subjective statements can spread false or misleading information, leading to incorrect conclusions.
- Bias: Subjective statements can perpetuate biases and stereotypes, influencing opinions and decisions.
- Polarization: Subjective statements can divide people into opposing camps, hindering constructive dialogue.
FAQ Corner: Which Statement Is Most Clearly Objective
What are the key characteristics of objective statements?
Objective statements are characterized by their reliance on facts, evidence, and verifiable information. They avoid personal opinions, emotions, and biases, and strive to present a balanced and impartial view of the subject matter.
How can we distinguish between subjective and objective statements?
Subjective statements express personal opinions, feelings, or beliefs, and are often characterized by the use of subjective language, such as “I think,” “I feel,” or “in my opinion.” Objective statements, on the other hand, are based on facts and evidence, and avoid the use of subjective language.
Why is objectivity important in language?
Objectivity in language is important because it allows for clear, accurate, and precise communication. It minimizes the impact of biases, promotes clarity, and ensures that messages are accurately conveyed and interpreted.