Chapter 48 billing and collections is the cornerstone of healthcare revenue cycle management, a complex and crucial process that directly impacts the financial health of healthcare organizations. This guide delves into the intricacies of billing and collections, providing a comprehensive understanding of the key concepts, best practices, and strategies.
From the initial billing process to effective collections management, denial management, and compliance, this guide covers every aspect of Chapter 48 billing and collections, empowering healthcare professionals with the knowledge and tools to optimize revenue and ensure financial stability.
Introduction to Chapter 48 Billing and Collections
Chapter 48 Billing and Collections delves into the fundamental aspects of billing and collection processes within the healthcare industry. It encompasses the principles, procedures, and techniques employed to manage financial transactions between healthcare providers and patients or insurance companies.
This chapter explores the key concepts of billing, including patient registration, charge capture, and claims processing. It also covers collection strategies, such as payment plans, dunning notices, and collection agencies. By understanding these concepts and principles, healthcare professionals can effectively manage the financial aspects of patient care and ensure timely reimbursement for services rendered.
Purpose and Scope
The purpose of Chapter 48 Billing and Collections is to provide a comprehensive understanding of the billing and collection cycle in healthcare. It aims to equip healthcare professionals with the knowledge and skills necessary to navigate the complexities of healthcare finance and optimize revenue generation.
The scope of this chapter encompasses the following key areas:
- Patient registration and account setup
- Charge capture and coding
- Claims processing and adjudication
- Collection strategies and techniques
li>Payment processing and reconciliation
Billing Process: Chapter 48 Billing And Collections
The billing process involves generating and sending invoices to customers for goods or services provided. It is a crucial aspect of revenue collection and plays a significant role in maintaining accurate financial records.
The billing process typically involves the following steps:
- Invoice Creation:The first step is to create an invoice that includes details such as the customer’s name, address, invoice number, date, description of goods or services, quantity, unit price, and total amount due.
- Invoice Delivery:Once the invoice is created, it needs to be delivered to the customer. This can be done through various methods, such as mail, email, or online portals.
- Payment Processing:When the customer receives the invoice, they are expected to make the payment as per the payment terms specified on the invoice. Various payment methods can be accepted, such as cash, check, credit card, or online payment gateways.
- Payment Reconciliation:Once the payment is received, it needs to be reconciled with the invoice to ensure that the correct amount has been received and that the customer’s account is updated accordingly.
- Follow-Up:In case of late or missed payments, follow-up actions may be necessary. This could involve sending payment reminders, contacting the customer directly, or initiating collection procedures.
Key Stakeholders
The billing process involves several key stakeholders, including:
- Customers:The primary stakeholders are the customers who receive the invoices and are responsible for making payments.
- Billing Department:The billing department is responsible for creating and sending invoices, processing payments, and reconciling accounts.
- Sales Team:The sales team is responsible for providing accurate information about the goods or services sold to the customers.
- Finance Department:The finance department oversees the overall financial operations, including billing and collections.
Best Practices
To ensure accurate and timely billing, it is important to follow best practices such as:
- Clear and Accurate Invoices:Invoices should be clear and easy to understand, with all necessary details included.
- Timely Invoice Delivery:Invoices should be delivered to customers promptly after the goods or services have been provided.
- Automated Billing System:An automated billing system can help streamline the process, reduce errors, and improve efficiency.
- Customer Communication:Clear communication with customers regarding payment terms and due dates is essential.
- Regular Reconciliation:Regular reconciliation of payments and invoices ensures accuracy and timely detection of any discrepancies.
Collections Process
The collections process involves a series of steps and strategies employed to recover outstanding payments from customers. It plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy cash flow and mitigating bad debts.
The collections process typically progresses through various stages, each with its own specific strategies and tactics.
Pre-Collections, Chapter 48 billing and collections
This stage involves proactive measures to prevent late payments and minimize the need for formal collections. It includes sending out timely invoices, offering early payment discounts, and establishing clear payment terms with customers.
Early Collections
When payments become overdue, early collections efforts aim to resolve the issue promptly and amicably. This stage typically involves sending out reminders, making phone calls, and exploring reasons for non-payment.
Late Collections
If early collections efforts prove unsuccessful, the process enters the late collections stage. This involves more aggressive strategies, such as sending out formal demand letters, imposing late payment fees, and exploring legal options.
Bad Debt
When all collection efforts have been exhausted, the outstanding debt may be considered uncollectible and written off as a bad debt. This decision is typically made after careful consideration of the costs and benefits of further collection efforts.
Use of Technology in Collections
Technology has revolutionized the collections process, enabling greater efficiency and automation. Collections software, for example, can streamline tasks such as tracking payments, sending reminders, and managing customer interactions.
Tips for Effective Collections Management
- Establish clear payment terms and communicate them effectively to customers.
- Monitor accounts receivable regularly and take prompt action on overdue payments.
- Use a combination of communication channels (e.g., phone, email, text) to reach out to customers.
- Be empathetic and understanding, while also maintaining a firm and professional approach.
- Consider offering payment plans or other arrangements to accommodate customers facing financial difficulties.
- Seek professional advice from a collections agency or attorney if necessary.
Denial Management
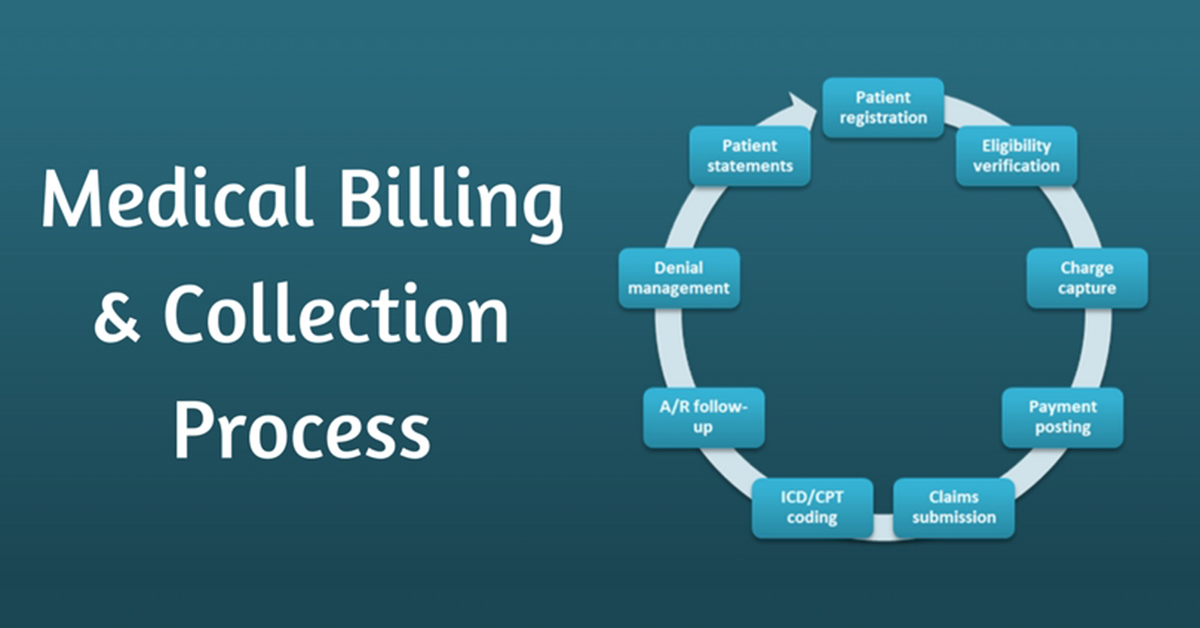
Denial management is the process of identifying, investigating, and resolving denied claims to maximize revenue recovery. Denials occur when insurance companies refuse to pay for healthcare services due to various reasons.
Types of denials include:
- Administrative denials: Incorrect patient information, missing documentation, or billing errors.
- Medical denials: Services not medically necessary, lack of supporting documentation, or incorrect coding.
- Contractual denials: Services not covered by the patient’s insurance plan.
To handle denials effectively, providers should:
- Review denials promptly: Investigate the reason for the denial and gather supporting documentation.
- Communicate with the insurance company: Contact the payer to clarify the denial and negotiate a resolution.
- File appeals: Submit a formal appeal with additional documentation to support the claim.
Strategies for Reducing Denials
To minimize denials, providers can:
- Verify patient eligibility: Ensure patients have active insurance coverage and confirm benefits.
- Obtain accurate patient information: Collect complete and correct patient demographics, insurance details, and medical history.
- Use correct coding: Utilize the appropriate medical codes and modifiers to accurately describe services provided.
- Document services thoroughly: Provide detailed medical records to support the necessity and appropriateness of services.
- Educate staff: Train staff on billing and coding best practices to reduce errors.
Reporting and Analysis
Reporting and analysis play a crucial role in billing and collections by providing valuable insights into the performance of these processes. By tracking key metrics and generating reports, healthcare organizations can identify areas for improvement, optimize revenue, and enhance patient satisfaction.
Key metrics to track include the following:
- Number of claims submitted
- Number of claims denied
- Average days in accounts receivable
- Percentage of collections
- Patient satisfaction scores
Reports that can be used to improve performance include the following:
- Claims aging report: This report shows the number of claims that are outstanding for a certain period of time. It can help identify claims that need to be followed up on.
- Denial analysis report: This report provides a breakdown of the reasons for denied claims. It can help identify patterns and develop strategies to reduce denials.
- Patient satisfaction survey: This survey can provide feedback on the billing and collections process from the patient’s perspective. It can help identify areas where improvements can be made.
- The False Claims Act (FCA) prohibits healthcare providers from submitting false or fraudulent claims to government health insurance programs.
- The Anti-Kickback Statute (AKS) prohibits healthcare providers from offering or receiving kickbacks in exchange for referrals or business.
- The Stark Law prohibits physicians from referring patients to entities in which they have a financial interest.
- The HIPAA Privacy Rule protects the privacy of patients’ health information.
- The HIPAA Security Rule protects the security of patients’ health information.
- Developing and implementing a compliance plan.
- Educating staff on compliance requirements.
- Regularly auditing billing and collections practices.
- Reporting any suspected fraud or abuse to the appropriate authorities.
Compliance and Regulations
The healthcare industry is heavily regulated, and billing and collections are no exception. There are a number of federal and state laws and regulations that govern how healthcare providers can bill and collect for their services. Failure to comply with these laws and regulations can result in significant penalties, including fines, imprisonment, and loss of license.
Some of the most important compliance and regulatory requirements related to billing and collections include:
Healthcare providers must be aware of these and other compliance and regulatory requirements and take steps to ensure that they are in compliance. Failure to do so can result in significant financial and legal consequences.
Staying Compliant
There are a number of things that healthcare providers can do to stay compliant with billing and collections laws and regulations. These include:
By taking these steps, healthcare providers can help to ensure that they are in compliance with the law and protect themselves from financial and legal penalties.
FAQ Corner
What is the scope of Chapter 48 billing and collections?
Chapter 48 billing and collections encompasses the entire revenue cycle process for healthcare providers, including billing, collections, denial management, reporting, and compliance.
What are the key stakeholders involved in the billing process?
The key stakeholders involved in the billing process include healthcare providers, patients, insurance companies, and clearinghouses.
What are the different stages of the collections process?
The collections process typically involves pre-collection, early collection, and late collection stages, each with specific strategies and timelines.
What is denial management?
Denial management refers to the process of identifying, analyzing, and resolving denied claims to maximize reimbursement and reduce revenue loss.
What are the consequences of non-compliance with billing and collections regulations?
Non-compliance with billing and collections regulations can result in penalties, fines, and even legal action.